KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The Hong Kong risk-based capital (HK RBC) regime aligns Hong Kong’s insurance industry with global standards while enhancing financial resilience and market stability by aligning capital coverage with risk measures.
- Western Asset’s proprietary HK RBC Calculator provides comprehensive market risk calculations, offering a clearer risk profile when assets are measured against liabilities.
- The Calculator supports currency hedging strategies by calculating capital requirements on both currency-unhedged and Hong-Kong-dollar-hedged bases, helping insurers efficiently manage currency risk.
- Granular analysis at both the portfolio and security levels allows for precise risk assessment and capital allocation with the benefit of security-level capital requirements aiding in issue selection.
- Return on capital is used to compare the capital efficiency of different strategies by identifying the most effective approaches for maximizing returns within regulatory capital considerations.
Background
Following multiple rounds of quantitative impact studies and public consultations by the Hong Kong Insurance Authority, the Hong Kong Risk-Based Capital (HK RBC)1 regime became effective on July 1, 2024. This regulatory framework marks a significant milestone in the evolution of Hong Kong’s insurance industry by aligning with global standards such as the Solvency II framework in Europe, the RBC frameworks in the United States and the International Capital Standard (ICS) being developed by the International Association of Insurance Supervisors (IAIS). The HK RBC regime aims to enhance the financial resilience of insurers by ensuring that they hold sufficient capital to cover their risks, thereby protecting policyholders and maintaining market stability.
HK RBC Framework Overview
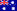
Exhibit 1 illustrates the basic modules of the HK RBC Prescribed Capital Amount (PCA). In managing efficient fixed-income portfolios, Western Asset focuses on a few of these modules. There are parts of the HK RBC framework that are exclusive to our insurance clients and are more relevant to their operations. However, some of these modules are essential for the prudent management of fixed-income and other portfolios. Despite Western Asset’s focus on fixed-income portfolios, we can also provide insurance clients with information about capital requirements associated with equity holdings to support broader portfolios.
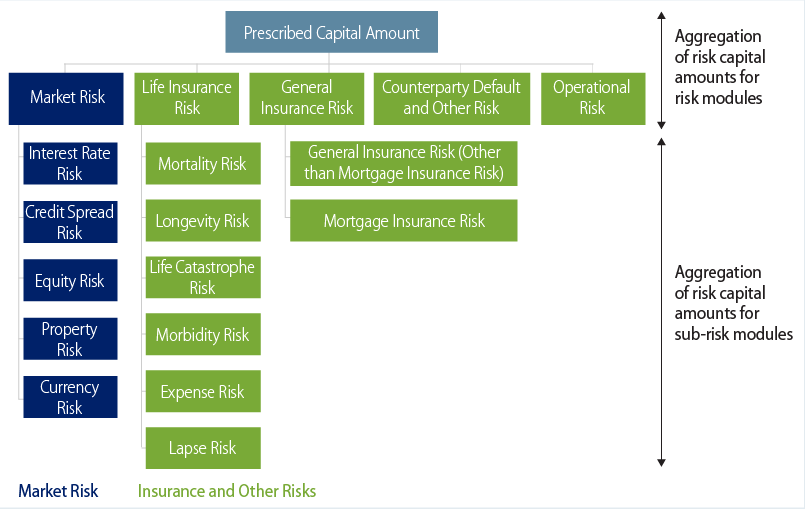
Interest rate risk, credit spread risk and currency risk modules are relevant to managing fixed-income portfolios in a capital-efficient way. These sub-risk components are aggregated based on a predetermined correlation matrix, as per the correlation formula:

*Where s and t are every pair of sub-risk modules.
As you can see in Exhibit 2, correlations under the lower interest rate scenarios are higher, reflecting heightened systemic risks during potential crisis scenarios.
Here we detail various aspects of credit spread risk, currency risk and interest rate risk as they relate to managing fixed-income portfolios.
Credit Spread Risk
We identify credit spread risk as the primary contributor to the risk charges within fixed-income portfolios, influenced by credit rating bands, remaining term to maturity and spread duration.
Credit spread PCA is determined by evaluating changes in net asset value (NAV) due to upward shocks in credit spreads. These shocks are applied additively, with the reduction in NAV representing the credit spread PCA.
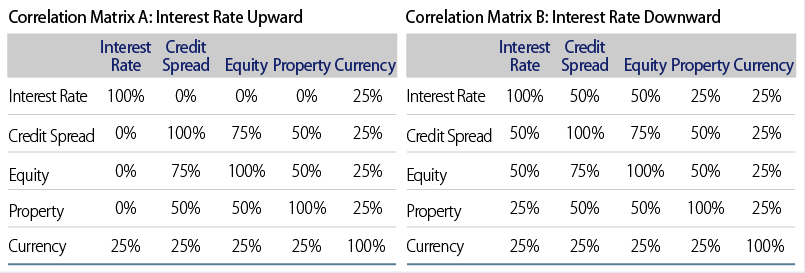
Certain asset classes receive preferential treatment, including zero credit spread PCA for specific sovereign bonds, bonds rated AAA or AA, and local government bonds issued in the Hong Kong dollar (HKD), euro (EUR), British pound (GBP), Japanese yen (JPY), Chinese renminbi (RMB), Singapore dollar (SGD), Thai baht (THB), New Taiwan dollar (TWD) and US dollar (USD). Recognized multilateral development banks or supranational organizations (Exhibit 3) are treated as sovereign bonds and recognized green bonds receive a 10% reduction in credit spread PCA. A recognized green bond must have pre-issuance external verification from an independent and qualified international third party confirming that it meets the green criteria or principles issued by the Hong Kong Insurance Authority.
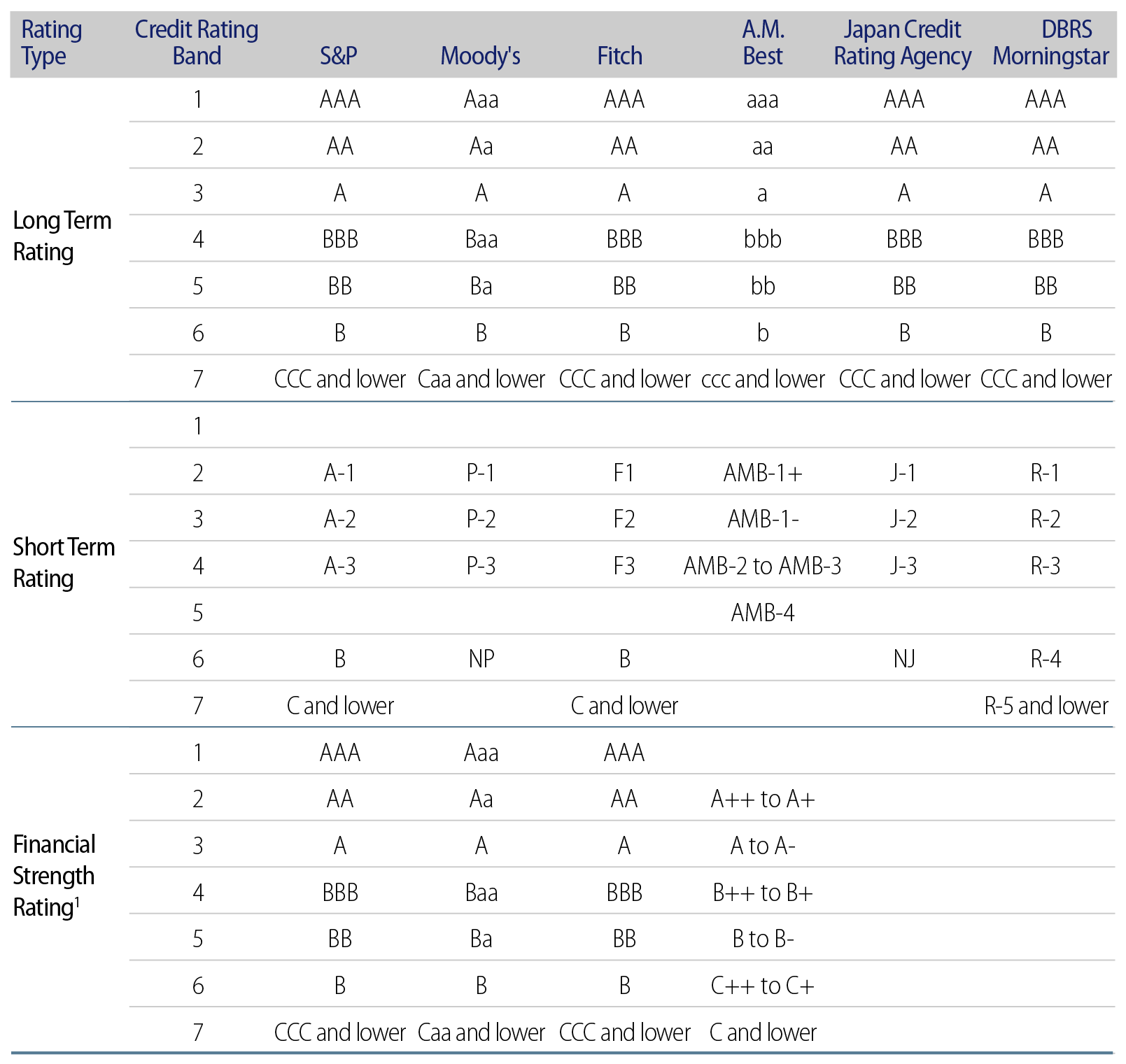
Within each credit rating band, uniform credit spread shocks are applied regardless of the more granular agency ratings.
We use an internally calculated spread duration to estimate the change in value of each security sensitive to credit spreads.
Currency Risk
For currency risk, the PCA is calculated by applying the determined PCA factor to the net long or short position of each currency. For currencies with negative hedging costs (i.e., when there is yield enhancement by hedging from those currencies back to HKD), capital efficiency is achieved due to higher yields and a zero currency PCA for the HKD. Conversely, for currencies with positive hedging costs, assessing the hedging cost versus each currency’s PCA can guide the hedging strategy.
Capital efficiency needs to be assessed in the context of specific portfolios, given that correlations play an important role. Western Asset can assist insurers in creating dynamic hedging strategies, particularly when hedging costs fluctuate, aiming for optimal capital efficiency under changing market conditions.
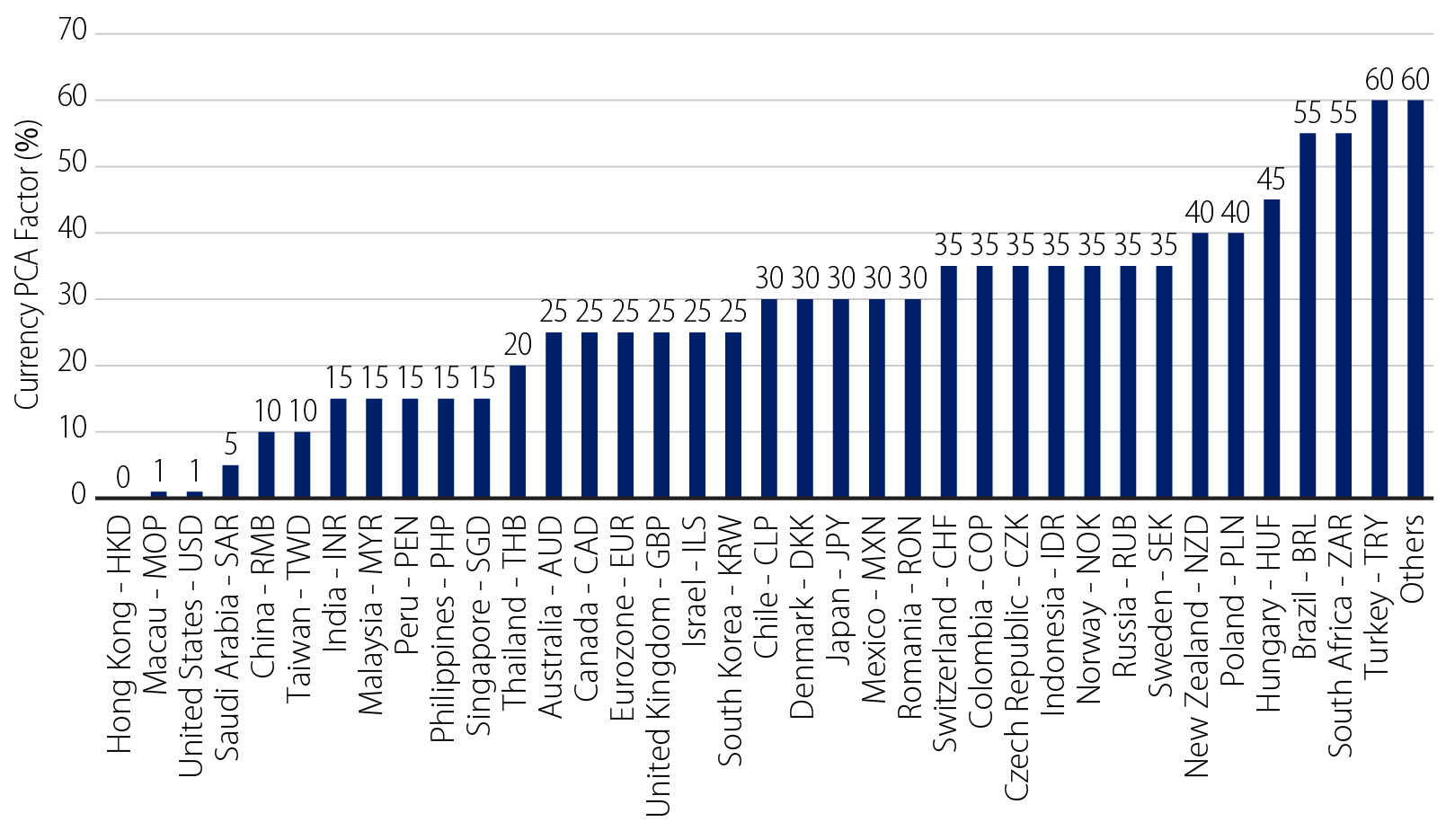
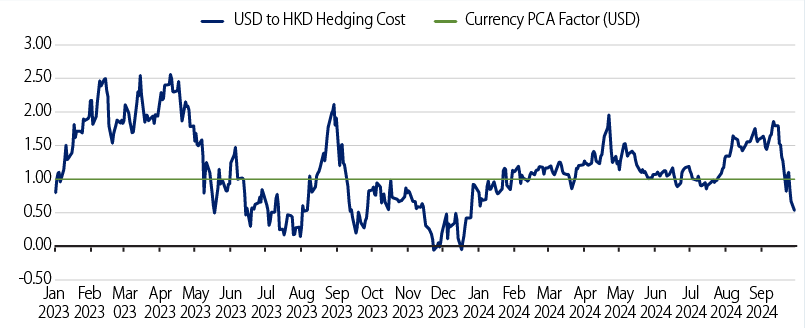
Exhibit 7 shows the behavior of USD to HKD hedging costs over time compared with the 1% PCA factor for the USD currency under HK RBC
Interest Rate Risk
Usually, insurers tend to work on their asset liability management to immunize interest rate risk derived from the mismatch between assets and liability cashflows. However, Western Asset also considers interest rate risk as part of a more comprehensive analysis.
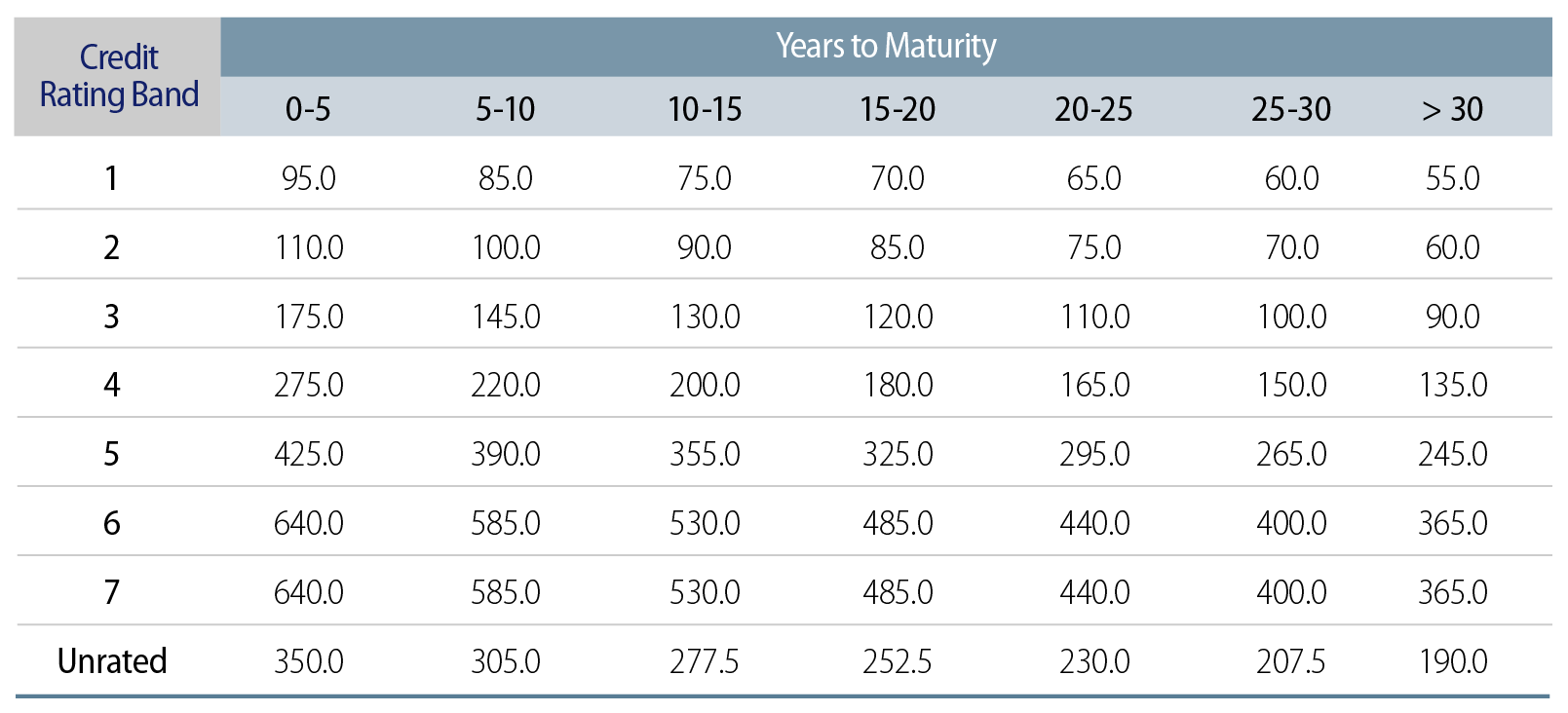
Interest rate PCA is determined by assessing changes in NAV resulting from upward and downward shocks to the risk-free yield curve for each currency, as prescribed by HK RBC. These shocks are applied multiplicatively, with the larger reduction in NAV under higher and lower interest rate scenarios representing the interest rate PCA. Notably, shocks are capped at ±200 bps and are not applied to any negative observable market rates.
Exhibit 8 shows the prescribed upward and downward interest rate shocks according to different security maturity bands. Even though the predetermined shocks decrease along with the term of the securities, the resulting interest rate PCAs increase as the term of the securities increase. We use effective duration from our suite of analytic tools to estimate the change in value of each interest-rate-sensitive security.

Western Asset’s Approach
Western Asset has meticulously assessed the rules of the HK RBC regime and developed a proprietary calculator for the HK RBC market risk PCA.
This advanced tool is designed to delve into the granular calculations of market risk PCA, enabling a detailed analysis of capital efficiency across various asset classes and investment strategies. By leveraging this Calculator, Western Asset enhances its capability to optimize portfolios under risk and capital constraints and identify attractive investment opportunities in an evolving market and regulatory environment. In managing insurance portfolios, investment trade-offs are not simply constrained to analysis of risk versus expected returns; capital efficiency is also critical in determining optimal portfolio composition for these portfolios.
Highlights of Western Asset’s proprietary HK RBC Calculator include:
- Comprehensive PCA Calculation: We calculate total PCAs from two perspectives including and excluding interest rate risk, given our aforementioned analysis that insurers tend to conduct their own asset liability management analyses.
- Currency Hedging Strategies: We calculate PCAs on both currency-unhedged and HKD-hedged bases. Given that the PCAs for different currencies vary under the HK RBC framework, Western Asset can assist insurers in creating dynamic capital hedging strategies to effectively manage currency risk.
- Granular Analysis: We calculate PCAs at both portfolio and security levels. Security-level PCAs are invaluable for issue selection, allowing for precise risk assessment and capital allocation decisions.
- Return on Capital: We define Return on Capital (ROC) as the ratio of yield to PCA. This metric is used to compare the capital efficiencies of different strategies and helps us to identify the most effective approaches for maximizing returns within the constraints of regulatory capital requirements.
Analyzing Capital Efficiency Under HK RBC
Using our proprietary Calculator, we conducted an in-depth capital efficiency analysis of various fixed-income asset classes, as listed in Exhibit 9. Hong Kong based insurers may want to consider these asset classes for their overall asset allocation.
The entire suite of holdings is processed through our proprietary analytics system, generating comprehensive metrics such as various yield measures, duration and spread duration. Additionally, the holdings are analyzed using our proprietary risk engine, WISER,2 which delivers a full spectrum of risk analytics including tail risk metrics like value-at-risk and expected shortfall at various percentiles, as well as both historical and forward-looking scenario analyses. This robust analytical framework enhances our ability to compare different strategies from a balanced perspective of return, capital and risk.
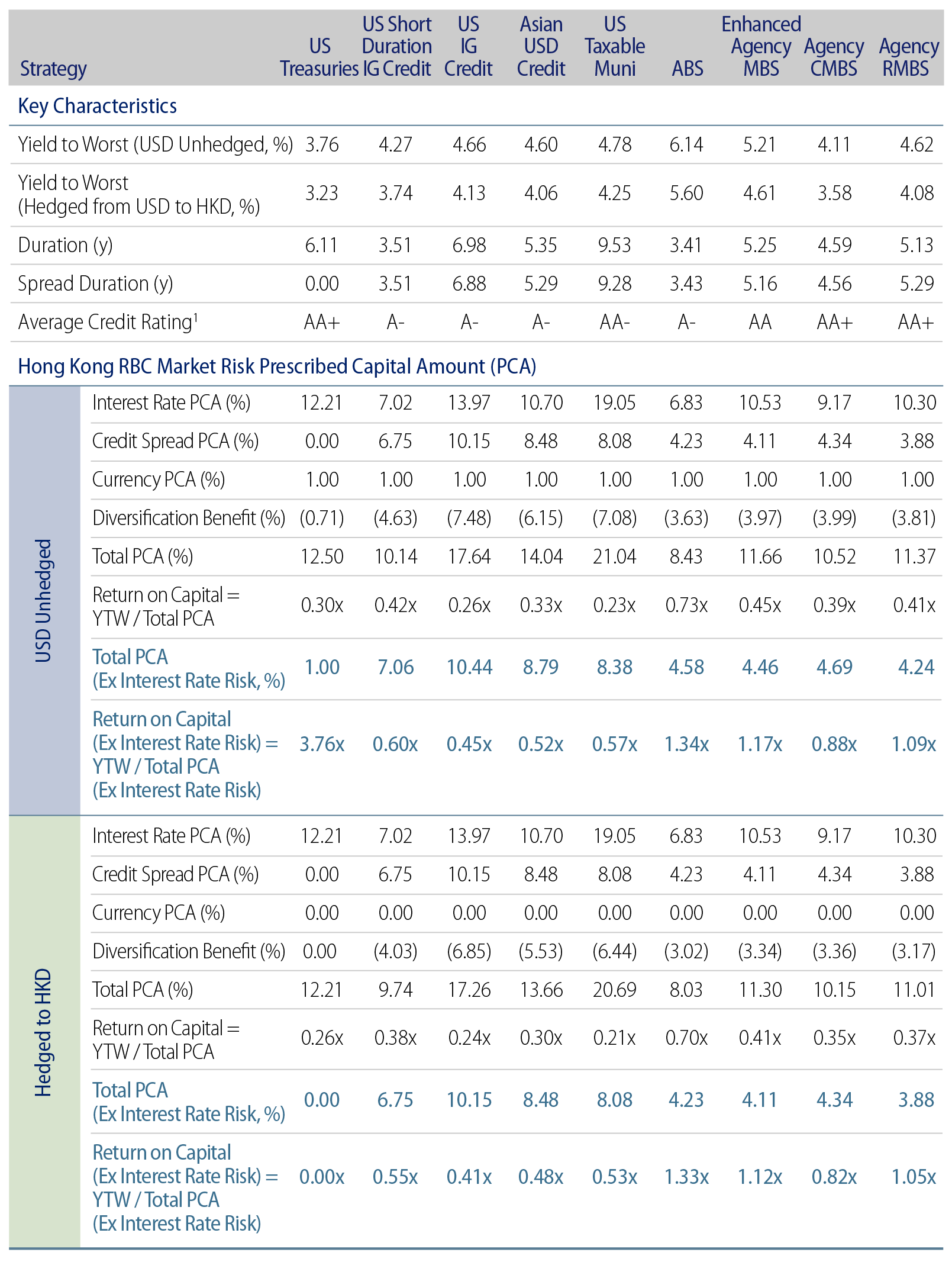
Exhibit 10 presents a summary of analytics and the HK RBC Market Risk PCA on both USD-unhedged and HKD bases for each of the asset classes considered. The use of asset classes in our analysis is done for illustrative purposes. Western Asset actively manages fixed-income portfolios with the aim of enhancing both their risk and capital efficiency. Essentially, dynamic rebalancing of a combination of these asset classes, along with strategic issue selection and sector selection within an actively managed portfolio, supports this goal.
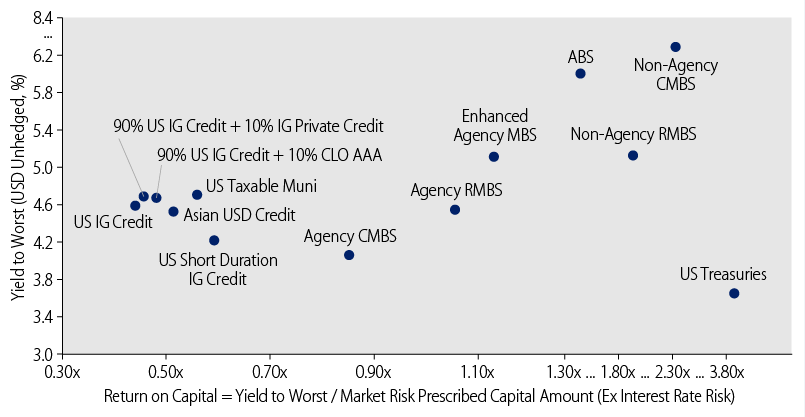
Exhibit 11 features a scatterplot of yield versus return on capital (ROC) under HK RBC. In this scatterplot, the horizontal axis represents what we define as ROC, calculated by dividing the yield-to-worst (YTW)3 by the market risk PCA excluding interest rate risk, while the vertical axis represents the YTW on a USD-unhedged basis.
Our analysis reveals several key insights:4
- Primary Risk Contributor: In terms of total PCAs excluding interest rate risks, credit spread risk is the primary contributor to the variance in risk charges across the selected asset classes and strategies. The credit spread risk charge is influenced by the credit rating band, remaining term to maturity, and spread duration.
- US Treasuries: The asset class with the highest ROC is USTs. Despite having the lowest yield at 3.76% on a USD-unhedged basis, it benefits from a 0% credit spread capital charge, making it highly capital-efficient.5
- Taxable Municipal Bonds vs. Corporate Bonds: High-quality taxable municipal bonds are preferred to corporate bonds in terms of capital efficiency under the market conditions as of the date of the analysis. For US investment-grade credit, the ROC is 0.45x excluding interest rate PCA, with a yield of 4.66% on a USD-unhedged basis. For US taxable municipal bonds, the ROC is 0.57x excluding interest rate PCA, with a yield of 4.78% on a USD-unhedged basis.
- Securitized Products: Except for bonds that meet specific conditions, the HK RBC framework does not differentiate between different types of asset classes (e.g., structured products and corporates) or issuers. As the HK RBC framework does not penalize securitized exposures in terms of credit spread risk charge, high-quality securitized products can lead to higher returns on capital due to their robust returns and the absence of additional capital penalties under the HK RBC framework. This treatment enhances capital efficiency, making securitized products an attractive option for optimizing investment performance while adhering to appropriate risk and capital constraints. From the analysis, the strategy with both the highest yield and ROC is the enhanced agency MBS strategy, with a ROC of 1.17 excluding interest rate PCA and a yield of 5.21% on a USD-unhedged basis.
By integrating these capabilities, Western Asset’s proprietary HK RBC Calculator offers a powerful tool for insurers to navigate the complexities of the new regulatory landscape, optimize their capital usage and seek to enhance their investment performance. This tool enables insurers to make informed decisions, while seeking to optimize capital efficiency and improved investment outcomes in varying market conditions.
The implementation of HK RBC in July 2024 represents a significant advancement in Hong Kong’s insurance regulatory landscape. This framework enhances insurers’ financial resilience and ensures robust policyholder protection. Western Asset’s tailored approach to managing fixed-income portfolios under HK RBC enables our insurance clients to optimize capital usage and the potential to investment performance, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements while seeking attractive risk-adjusted returns and maximizing capital efficiency.
A Word on Equities
Equity PCA is determined by evaluating the reduction in NAVs by applying the adjusted equity downward stress factor, which is sensitive to changes in equity market prices or volatility.
For developed market listed equities, emerging market listed equities, portfolio investments with no look-through, and other equities, the sum of the equity downward stress factor corresponding to the type of equities and the most recent countercyclical adjustment (CCA) specified by the Hong Kong Insurance Authority is used in our proprietary Calculator, as shown in Exhibit 12. For non-regulated investments in affiliates (if not consolidated) and strategic investments, the equity downward stress factor corresponding to the type of equities is applied. The CCA is capped at ±10% as determined by the regulator.
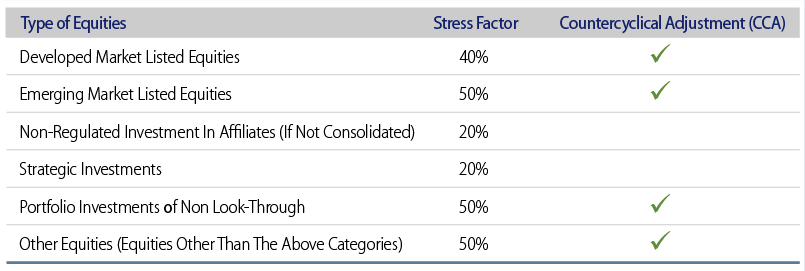
Where an equity is listed as secondary, the stress factor must be applied based on the exchange on which the equity has its primary listing.
Conclusion
The adoption of the HK RBC regime aims to enhance the financial resilience of insurers, maintain market stability, and safeguard the interests of policyholders. Western Asset’s tailored approach to HK RBC enables our clients to optimize their capital usage and adopt investment strategies that seek to obtain superior risk-adjusted returns in a capital-efficient way. By leveraging our expertise and proprietary tools, we work in partnership with insurers, navigating the complexities of this new regulatory landscape and capitalizing on opportunities for growth and improvement for our clients.
ENDNOTES
1. Hong Kong Insurance Authority. https://www.ia.org.hk/en/supervision/reg_insurers_lloyd/an_overview_of_the_risk_based_capital_regime.html
2. Western Information System for Estimating Risk
3. Yield-to-worst (YTW) is the lowest potential yield that can be received on a bond without the issuer actually defaulting.
4. The insights of the analysis are dependent on the market conditions as of 30 September 2024.
5. Since US Treasuries are USD-denominated, there is a 1% currency PCA charge.