Municipals Posted Negative Returns During the Week
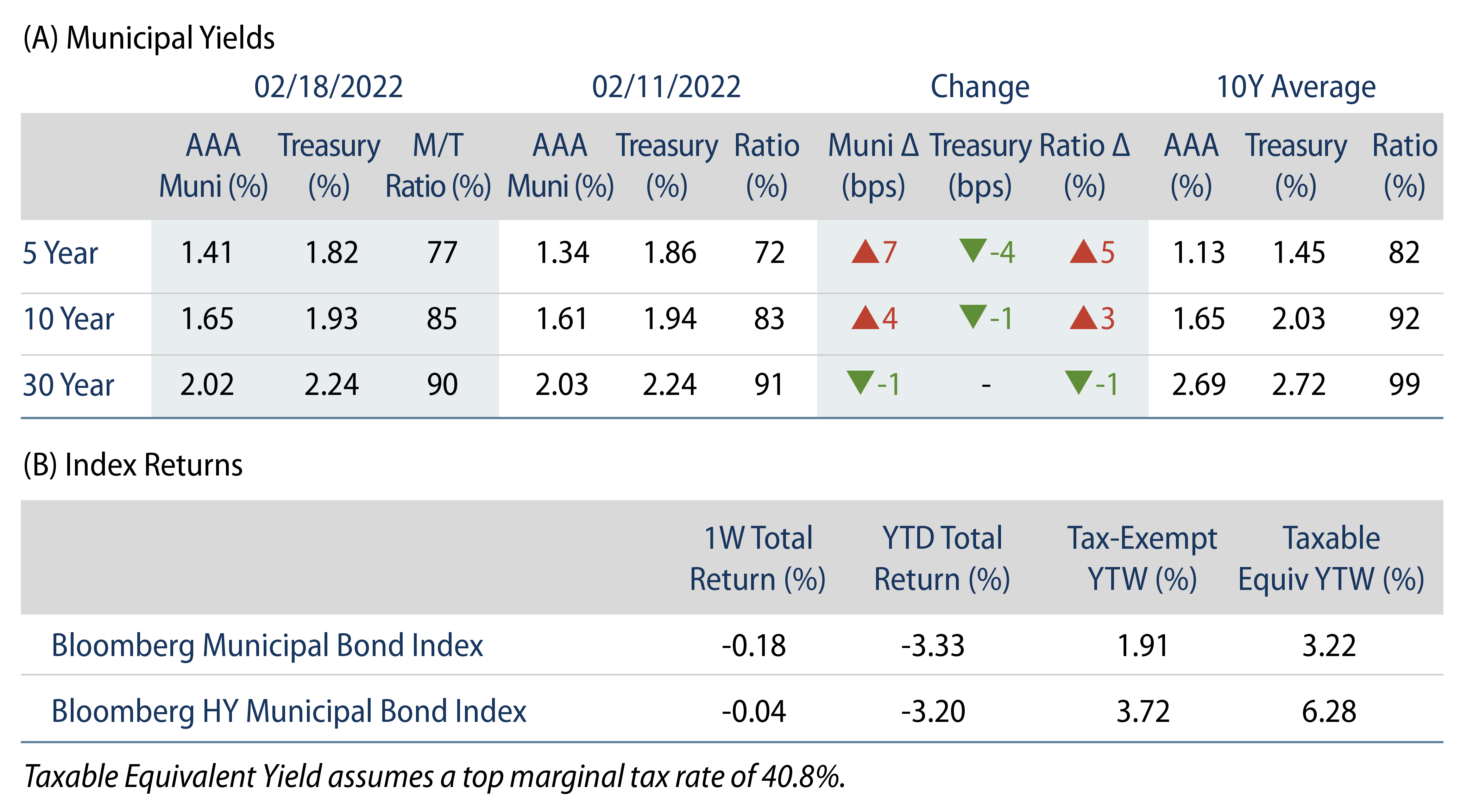
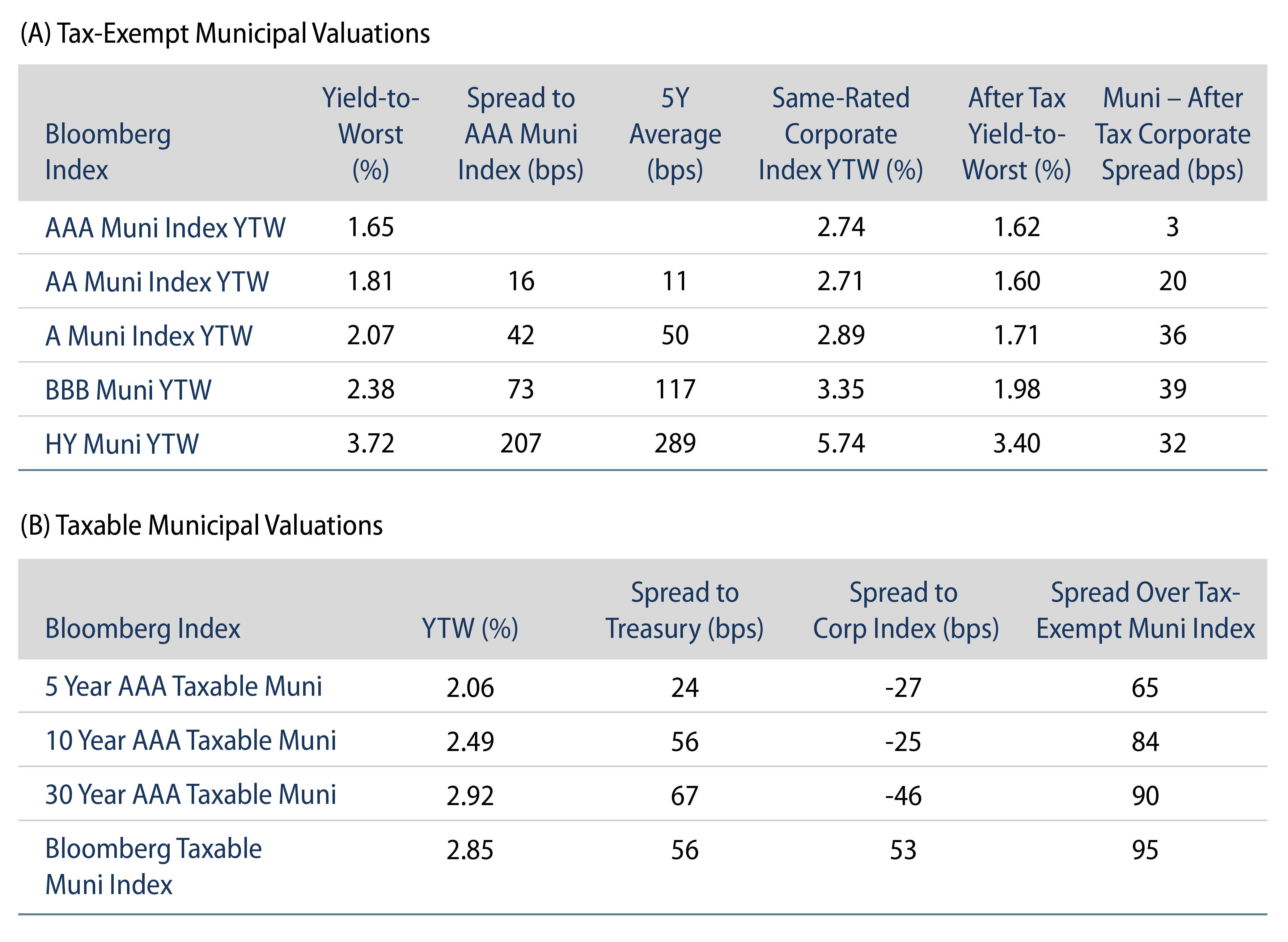
US municipals posted negative returns during the week and generally underperformed Treasuries as ratios moved higher in the short and intermediate part of the yield curve. High grade municipal yields moved 4-7 bps higher in short and intermediate maturities as the curve flattened. Demand for tax-exempt munis remained weak as municipal fund outflows persisted. The Bloomberg Municipal Index returned -0.18%, while the HY Muni Index returned -0.04%. This week we highlight the impact of labor shortages on the health care sector.
Weak Technicals Were Driven by Mutual Fund Outflows, Partially Offset by Limited Issuance
Fund Flows: During the week ending February 16, weekly reporting municipal mutual funds recorded $1.3 billion of net outflows, according to Lipper. Long-term funds recorded $1.2 billion of outflows, high-yield funds recorded $776 million of outflows and intermediate funds recorded $114 million of outflows. Municipal fund outflows year to date (YTD) extended to $7.2 billion.
Supply: The muni market recorded $5.6 billion of new-issue volume, down 28% from the prior week. Total YTD issuance of $49 billion is 13% higher from last year’s levels, with tax-exempt issuance trending 45% higher year-over-year (YoY) and taxable issuance trending 56% lower YoY. This week’s new-issue calendar is expected to remain below average at $4.3 billion given the holiday-shortened week. Largest deals include $1.1 billion Virginia Small Business Financing Authority and $412 million Nature Conservancy transactions.
This Week in Munis—Labor Shortages Hit Health Care
The municipal market has not been immune to the labor market shortage impacting the broader US economy. While January nonfarm payrolls remain just 1.9% below pre-pandemic peaks, state and local payrolls remain 3.7% (718,000 jobs) below the pre-pandemic peak, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. This week we explore the health care sector, where health care payrolls remain 3.0% below pre-pandemic levels, despite increased demand for services observed in the sector.
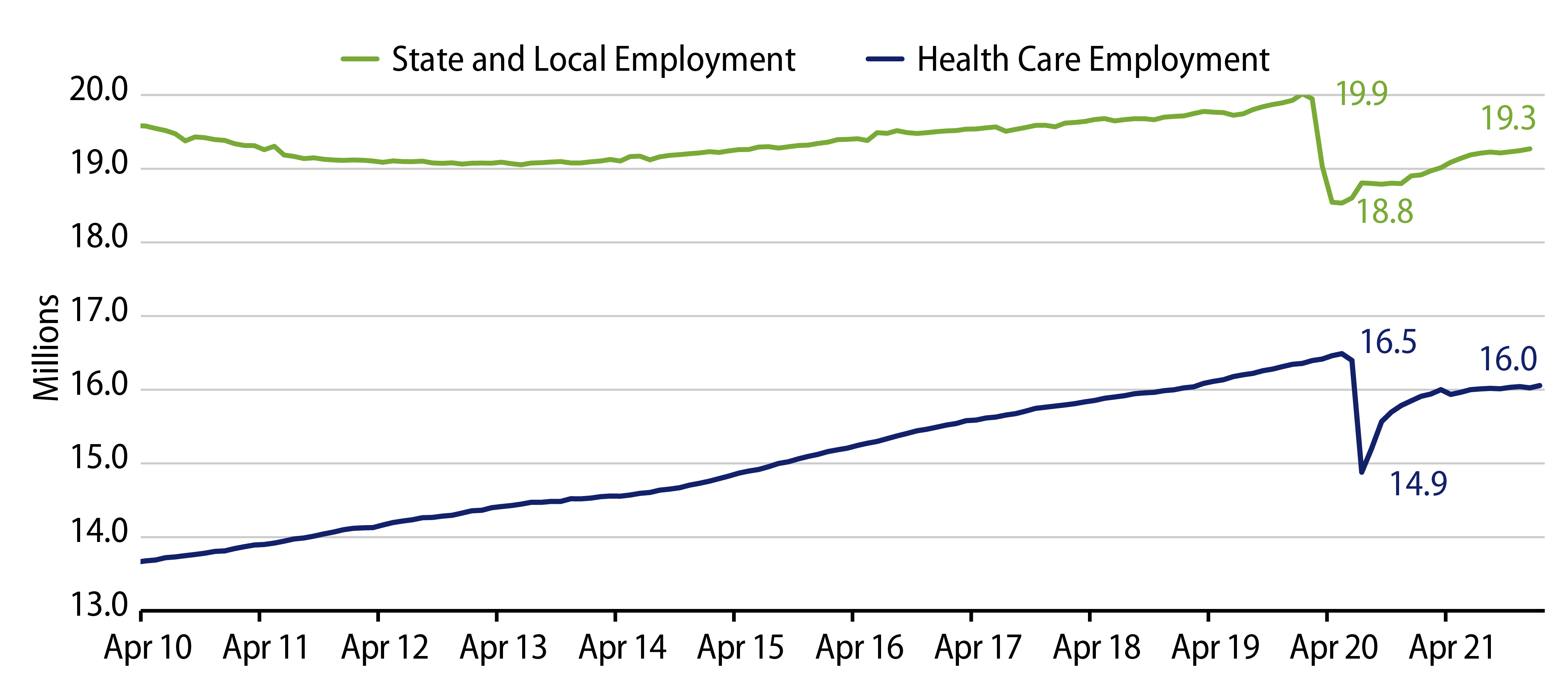
Health care operations are labor intensive, with salaries, wages and benefits typically accounting for half of a hospital’s operating expenditures. Many health care systems were challenged by labor shortages entering the pandemic, driven by a dearth of qualified nursing candidates relative to the growing demand for services. Elevated demand for health care services throughout the pandemic period and the more recent rebound of elective services have further magnified labor shortages in the sector. Employee turnover has risen due to taxing working conditions, opposition to vaccine mandates, and elevated competition from other sectors. Hospitals already operate on relatively modest margins, and financial performance may be affected if labor shortages contribute to rising labor costs.
Considering current valuations paired with improving demand for services and longer-term demographic trends, Western Asset is constructive on the health care sector. However, we tend to favor larger systems that benefit from operational scale and strong balance sheets, which should provide flexibility in the challenging environment. We expect these larger systems to have better access to talent and be in a better position to provide solutions that drive labor force stability. Over the longer term, we will focus on how the sector addresses its labor shortages, which we anticipate could be a mix of increasing immigrant hiring and utilizing technology to better allocate resources. Meanwhile, we are cautious on smaller hospitals, assisted living facilities and continuing care retirement communities where we have recently observed increased defaults due to unfavorable volume trends that have been exacerbated by higher costs at least partly attributable to labor shortages.